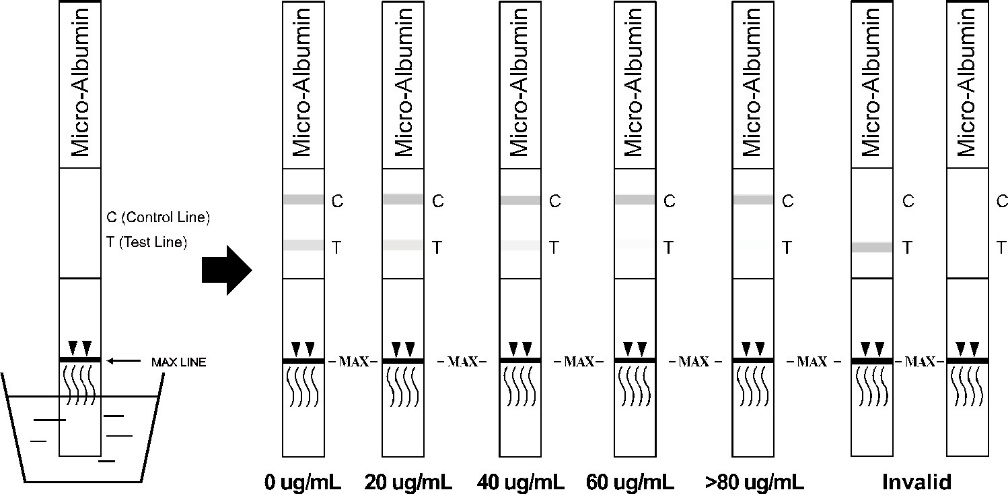
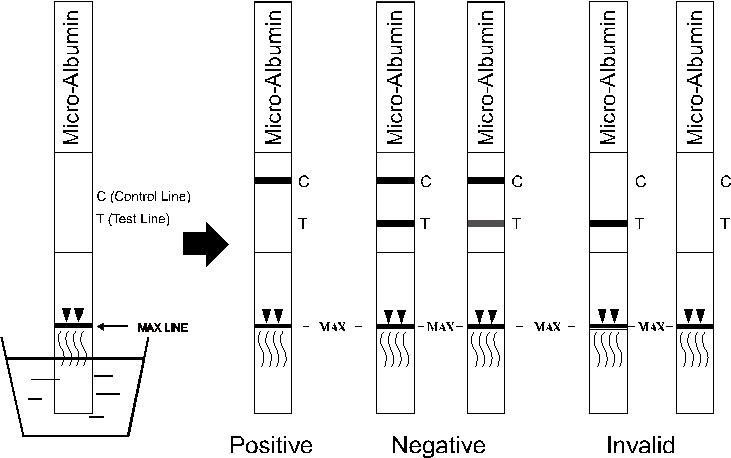
The persistent appearance of small amounts of albumin in urine (microalbuminuria) may be the first indicator of a renal dysfunction. For diabetic patients, positive results may be the first indicator of a diabetic nephropathy. Without therapy, the amount of released albumin will increase (macroalbuminuria) and renal insufficiency will occur.